Standby Medical Personnel: The Requirements of Training.
The largely unrecognized heroes in the realm of emergency and event medicine are standby medical staff. Be it a big public event, a sport event, a concert, a risky working zone, these medics are always ready: they are to swing into action as soon as an emergency issue emerges. But what does it take in order to be a part of this critical frontier? How is this training developed to create such a diverse pool of professionals ready to work in various medical situations?
This blog will examine the kind of training, certifications and hands on experience required of standby medical staff. Are you aspiring to become an EMT or an event manager wondering how they should prepare and be compliant with the regulations, this guide explains it all.
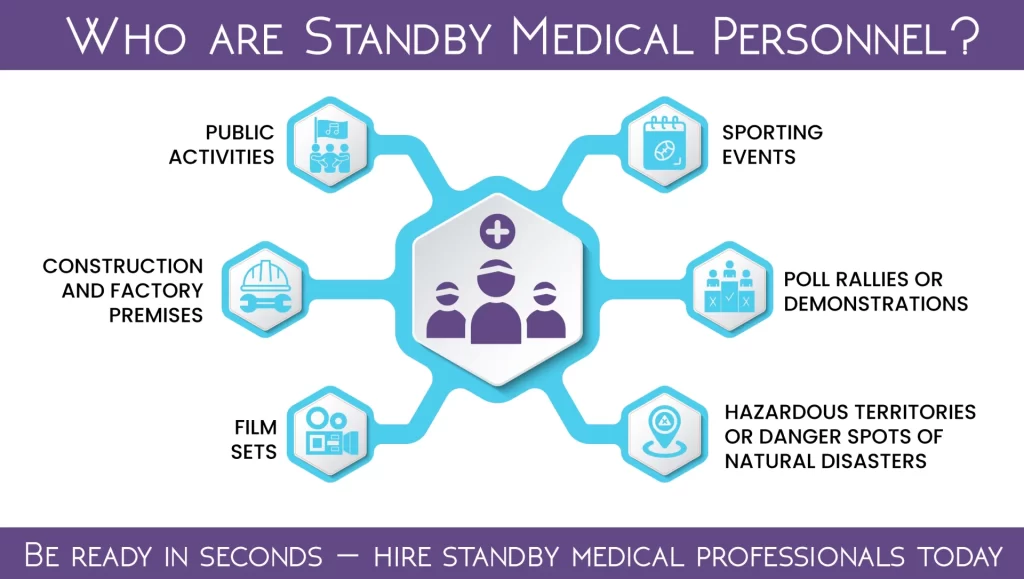
Who are Standby Medical Personnel?
Standby medical staff are professionals who have been trained in medicine to avail direct medical services on demand upon the provision of a schedule on an event or site. They are there not because medical emergency is likely to happen, but because it may happen the next time and seconds are precious.
The common scenarios that involve standby medical personnel are:
- Public activities (fests, music festivals, marathons)
- Construction and factory premises
- Film sets
- Sporting events
- Poll rallies or demonstrations
- Hazardous territories or danger spots of natural disasters
The Importance of the Right Training
Standing on standby does not imply waiting around. It is all about being ready to anything, a scratched knee, to a complete cardiac arrest. Training helps to make sure that the personnel:
- Taking fast and accurate medical decisions
- Exercise legal and ethical procedures
- Compact use of emergency equipment
- Use on-site messages and provide communications with external responders
- A medically unmatured responder is a danger to people. That is why intensive training is a must.
The standby team can consist of such emergency treatment specialists as EMTs, paramedics, nurses, and even physicians, depending on the level of risk of the event.
Core Certifications Needed
Most of the standby medical positions start with the requirement of being an Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) or more. In response to the risk level of the event or the standards of the organization in question, the personnel might also require:
1. EMT-Basic Certification (EMT -B)
Time frame: 120150 hours
Topics Covered:
- Patient assessment
- CPR/AED use
- Airway management
- Hemorrhage control
- Spinal injury and Fracture care
2. Advanced EMT (AEMT)
The skills in EMT-B and adds:
- IV therapy
- Basic pharmacology
- Adventured air way methods
3. Paramedic Certification
Length: 1,200 1,800 hours
Focuses On:
- Advanced cardiac life support (ACLS)
- Pediatrics Advanced Life Support (PALS)
- Drugs administration and pharmacology
- Endotracheal intubation
- EKG interpretation
4. CPR and First Aid Certificate
Even positions that do not involve EMT (e.g. security or event personnel) may expect the latest CPR and basic first aid certification to be up to date.
5. Specialized Certifications
It might also be necessary, depending on the event to have the following:
- Wilderness First Responder (WFR)
- Awareness/Operations Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT)
- Bloodborne Pathogen Training
- Tourniquet training
- Incident Command System ICS Training
Other Non-Certification Skills
Although it is crucial to have them certified, certified standby staff is more than what lies in a book. Certain essential soft skills and situational skills are:
1. Scene Assessment Triage
The identification of risks, prompt identification of injuries and decision making of priority in treatment in mass casualty incidents are crucial.
2. Communication
They have to communicate effectively with:
- On site teams (security, fire marshals)
- Dispatch centers
- Ambulance crews
- Families of patients
- At least in his vision
3. Thinking with the Pressure
Whenever there are uncertain situations, a proficient skill to make a prompt and effective intervention selection can save a life.
4. Movement and Heat Physicals
Standby responders are faced with a possibility of having to carry heavy equipment, move through crowds or have to perform CPR for long hours.
5. Documentation
Each medical incident should be documented properly in terms of legal, medical and liability implications.
Equipment Training
Some of them merely know how to do things, but how to operate the tools, also. The standby staff should be competent in:
- Automated External Defibrillation (AED)
- Trauma kits (bandages, tourniquets and splints)
- Delivery of oxygen systems
- Stretcher and spine boards
- Drugs (within the scope of the practice)
This equipment is used on a regular basis to train and simulate many teams.
On-the-job Training and Shadowing
Most medical standby firms also insist that their newly hired employees should also go through the probation period on supervised shifts. In this period the personnel:
- Observe the manner in which experienced responders tackle different situations
- Find out how to move around the particular the venue or the event structure
- Get to know local procedure and reporting mechanisms
- This informative practice bridges the real life to theory chasm.
Continuing Education and Refresher Course
Certifications are not a one time affair. Medical personnel on standby are required to renew their licenses once in a while. This includes:
- CPR recertification (once in 1-2years)
- EMT/Paramedic continuing education units (CEU)
- New skills update (e.g. bleeding control kits, mental health crises)
- Best practices are not only required by regulations, but they are a patient safety issue.
Training on Law and Ethics
The standby medical responders are required to act within legal boundaries of practice. These covers being trained in:
Good Samaritan laws
- HIPAA and confidentiality of patients
- Affirmation and denial of treatment
- Liability reporting and documentation and Incident reporting
There are also in-house legal briefings which are given by a significant number of employers particularly in high profile or high-risk events.
Mental Health & Emotional Strength
It is emotionally demanding to handle traumatic injuries, unresponsive patients, or lawless scenes. Certain training courses have introduced a training course on:
- Stress management
- Peer support mechanisms
- Critical Incident Stress Debriefing (CISD)
- Burnout prevention
This assists in enhancing not only the wellbeing of the responders but also job retention and performance.
Environment-Specific Environment Training
The working environment of standby medical workers is always different and unpredictable. Training is frequently tuned that way:
1. Sporting Events
- Concussions, broken bones and sprains
- Dehydration and exercise related heat stroke
- Sideline navigation and crowds location
2. Construction/Industrial Sites
- Machineries or falls trauma
- Confined space recoveries
- Burns and chemical exposure
3. Festivals and Concerts
- Medical emergence with drugs and alcohol
- Trampling injuries
- Behavioural episodes
4. Film Sets
- Long hours of work
- Special effects injuries (e.g. burns, mishaps with the use of prosthetics)
- Rapid communication with safety teams in the field.
5. Remote Locations
- Late admissions in hospitals
- Evacuation logistics
- Improvisation and wilderness first aid
Dynamics and leadership training Teams
The standby medical services are seldom single-handed jobs. Efficient teamwork and leadership are important. Some of the organizations comprise:
- Training in chain-of-command
- Radio communications code of conduct
- Multi-casualty trainings
- Advanced leadership training of EMTs/Paramedics
- Reporting Systems and Technology
Reporting Systems and Technology
Digital tools are applied by modern standby teams in order to:
- Real-time Incident logging
- GPS and geofencing of the areas of events
- Hospital-to-hospital Patient Handoff
There is training on such platforms, which makes operations smoother and the accuracy of data.
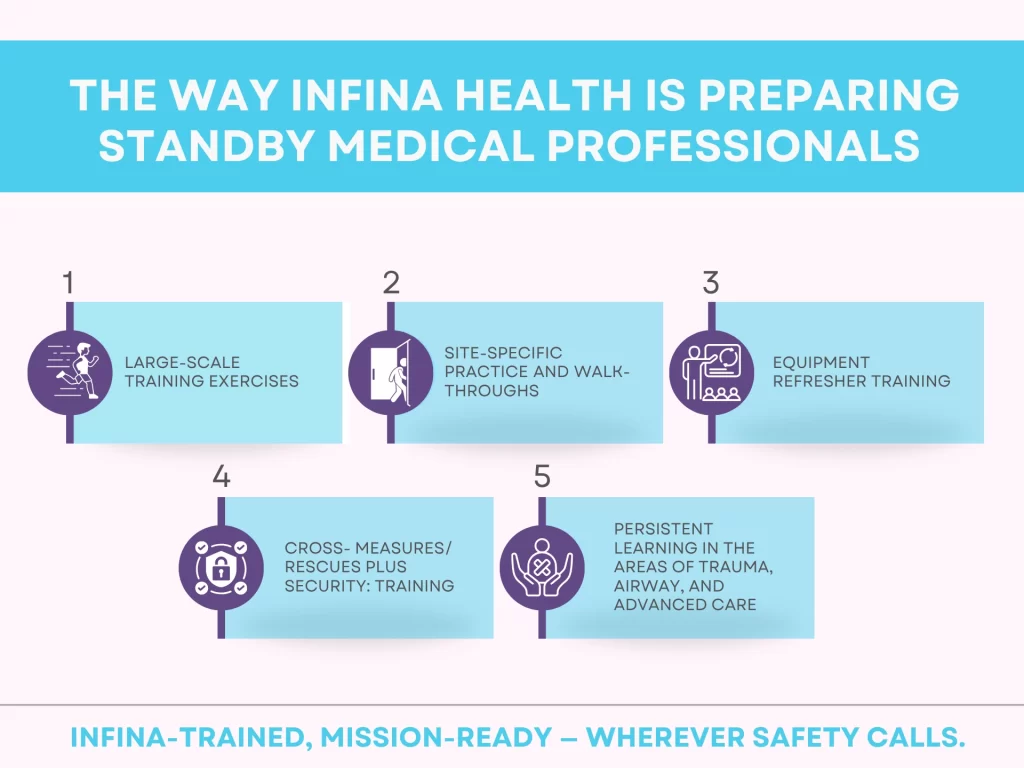
The Way Infina Health Is Preparing Standby Medical Professionals
They were training achievements on the part of Infina Health, where we boast of going an extra mile. Our standby people finish:
- Large-scale training exercises
- Site-specific practice and walk-throughs
- Equipment refresher training
- Cross- measures/ rescues plus security: training
- Persistent learning in the areas of trauma, airway, and advanced care
They can be found at a county fare, a film set, a critical incident zone– in any case, Infina has its teams trained, licensed, and full of readiness.
Final Thoughts
Standby medical pre-employment training does not represent a mere list of requirements, it is an act of dedication to quality, to safety, and to quick and expert treatment. These responders never sit and await incidents to happen; they remain at the forefront to be ready to handle the situation when a disaster hits.
Be it when planning an event or even looking forward to pursuing a career in this line of work, it is important to know the level and scope of training that is involved. Prepared properly, standby medical staff does not only help, but they also save lives.