Prioritization Life-Threatening Conditions by EMTs
This is because with emergencies, time is of the essence. Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) have the responsibility of making decisions in the blink of an eye, which might imply life or death. However, how do EMTs determine what patients require attention first when there are multiple injuries or indeterminate conditions?
This article examines the equipment, education, and mechanisms available to EMT to help them diagnose and treat life-threatening conditions as quickly as possible. Trauma triage, vital sign assessment, and so much more, you will discover what informs their instant decision-making in the worst of times.
What is Triage and Why Does It Matter?
Emergency medicine is based on triage. Triage derives the French term trier (to sort) and can be defined as the process of making quick evaluations of patients to decide how urgent their conditions are.
Triage enables EMTs in a pre-hospital and a hospital setting to:
- Identify people requiring urgent attention immediately
- Resource allocation in an efficient manner
Triage priority has normally three levels:
- Immediate (Red): Life threatening injuries that need immediate attention
- Delayed (Yellow): Serious yet is not life threatening at the present
- Minor (Green): Walking wounded or cases that are not life-threatening
- Deceased/Expectant (Black): No life or non-survivable injury can be found.

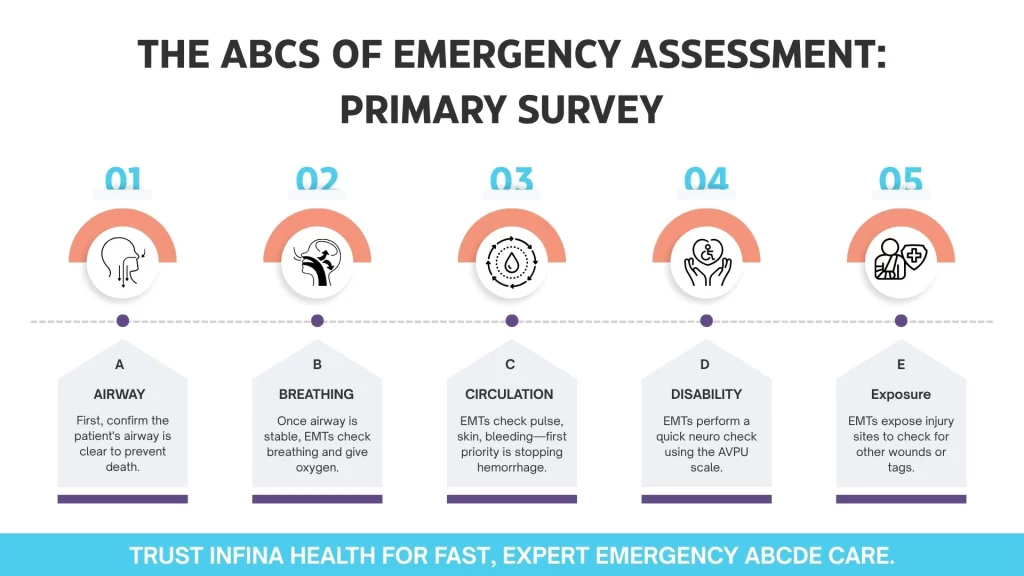
The ABCs of Emergency Assessment: Primary Survey
After EMTs arrive at a patient, their assessment starts with a primary survey, the quick evaluation method aimed at the most crucial functions. The method is sometimes recalled in terms of the ABCs of this system:
A – Airway
As a priority, the first thing you need to do is to confirm that the airway of a patient is open and clear. Interference, i.e. blood, vomit or the tongue (in unconscious people in particular), may easily result in a death.
B – Breathing
After the airway is stable, the EMTs will observe whether the patient is breathing properly. Particularly, they observe such indicators as chest rise, respiratory rate, and symptoms of distress (e.g., wheezing or gurgling). Administration of oxygen is done when it is needed.
C – Circulation
Among the circulation assessments performed by EMTs are:
- Pulse (quality and rate)
- Color and temperature of the skin
- Major bleeding presence
First of all, the priority is to stop severe hemorrhage. The EMTs can control bleeding with pressure, tourniquet or hemostatic dressings.
D – Disability
Then a brief neurological assessment is performed: Is the patient awake? Are they able to react to things? AVPU scale is used by EMTs:
- Alert Verbal response
- Pain response Unresponsive
E – Exposure
In order to properly determine the extent of the injury, EMTs will uncover any affected parts to ensure the existence of other lines of injuries or medical tags (such as allergy bracelets or diabetic ID).
Secondary Survey Head-to-Toe Check:
After stabilizing life-threatening conditions, EMTs is followed by secondary survey consisting of:
- Meticulous physical Examination
- Taking the patient history: the SAMPLE method:
- Signs and symptoms
- Allergies
- Medications
- Precedent history
- Last meal
- The incidence antecedents
The secondary survey will also make sure that all the unseen injuries are not overlooked but keep constant watch on the vital signs and the patient consciousness.
EMT Response to Certain Conditions that are Life Threatening
Now, upon reviewing how EMTs deal with some of the most common life-threatening emergencies specifically, let us examine how EMTs particularly deal with and or manage these situations:
1.Cardiac Arrest
· Immediate CPR AED (Automated External Defibrillator) use
· Ventilation and management of airways
· High speed transport and continued resuscitation
2.Extreme Trauma (e.g. Car Accident)
- Spinal protection of the neck
- Bleeding control
- Shock management
- The backboard or splint immobilization
3.Stroke
- Rapid appraisal of FAST (Face, Arms, Speech, Time)
- Prior movement to a stroke center
- Oxygen, IV access, as in protocol
4.Breathing Difficulty (e.g. Asthma, COPD, Anaphylaxis)
- Oxygen therapy
- Prescription medication giving (e.g. inhalers, EpiPen)
- Deterioration surveillance
5.Seizures
- Prevention of injury in convulsions
- Management of airway after seizure
- Observing post-ictal confusion, or a further seizure
In times when seconds make a difference, you can count on the skills and speed of the EMTs of Infina Health. Our team is trained to do critical care on the move, whether it is cardiac arrests or major trauma. Get in touch with us by calling now or booking at
www.infinahealth.com
Mass Casualty Incident (MCI) Prioritizing
EMTs implement Mass Casualty Triage Systems, including those shown in events where multiple patients may be involved: accidents, shootings, natural disasters, etc:
START Triage Simple Triage and Rapid Treatment)
EMTs assess:
- The ability to walk (green tag)
- Respirations (>30/ min = red tag)
- No perfusion (Cap refill >2 sec = red)
- Mental status (cannot follow orders = red)
The protocols will ensure a rapid triaging of patients prioritizing the most critically needy ones, which can be achieved despite the scarcities of personnel and equipment.
Protocol and Medical Direction Use of EMTs
EMTs do not act based on instinct. They adhere to medical protocols- a series of treatment courses that have already been approved by the medical director of their EMS system.
Examples of uniform procedures are:
- Pack of chest pain: It involves use of aspirin and monitoring of the heart
- Emergencies of diabetes: Blood sugar and dextrose gel or IV treatment
- Sepsis protocol: Speedy transport, oxygen, fluid procedures
EMTs are allowed to consult a physician through online medical control when they are uncertain about making certain treatment decisions.
Constant Checking and Reevaluation
Stabilization is not a once only affair. The health of the patient is evaluated by EMTs every moment. They track:
- Alterations in breathing, pulse, memory and consciousness
- Treatment response (e.g, oxygen, medications)
- Development of new symptoms or exacerbation of the old ones
Reassessment also allows one to realize that the patients are deteriorating early and improves the interventions accordingly.
Hospitals and Care Teams Communication
Another important factor of prioritization is being able to communicate clearly. EMTs call up the receiving hospital with a report by radio or telephone, summarizing:
- Patient condition
- Vitals
- Interventions
- ETA (estimation of arrival time)
This gives the emergency department an opportunity to get trauma rooms ready, notify specialists, or get code teams into action, as necessary.
Important Equipment and Tools That Assist EMTs in Priorities
- Oxygen saturation pulse oximeters
- Diabetic emergencies glucose meters
- Arrhythmia or Heart attack monitors
- Assisted ventilation bag valve masks
- Tourniquet and hemorrhage pressure dressing TT
- Trauma spinal immobilizing equipment
The accessibility and application of those tools are important aspects of prioritizing patient care correctly and in time.
How EMTs Practice Prioritizing in Stress
EMTs receive high-level training which covers:
- Lessons on anatomy, pathophysiology and procedures in the classroom
- Trauma and mass casualty incident simulation simulations
- Field experience by experiencing ride-along trips with the ambulance teams
- Continuing education in order to remain abreast with best practices
This skill of keeping one cool, thinking on one’s feet and making quick decisions is the output of both training and experience.
Why Prioritization is Lifesaving
In the case of lack of prioritization:
- Delayed care may result to death of patients who have survivable conditions
- There is a possibility of misallocation of resources
- There can be a deterioration of outcome, despite otherwise successful therapies
- The first most important part of the chain of survival is the EMTs.
They save lives way before patients can even want to reach the hospital by quickly determining who is in the worst need of help and going there.
Conclusion
Emergency medical technicians can be called unsung heroes of the emergency care system. With their training, and experience, and the ability to help at all times, they put a premium on life-endangering injuries with speed and diligence. No matter what the catastrophe may be car crash, heart attack, or mass casualty event, EMTs will know how to sort, assess and act.
Our EMTs at Infina Health have been trained to provide quick, competent, and humane care that is needed the most. We ensure your safety and health on the forefront whether it is an emergency transport, an event standby, or a non-emergency service.
To discuss our emergency medical services and what Infina Health is prepared to offer your community, call our offices now: 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.