The Management of High-Risk Patients by Critical Care Teams: The Reality of Life Saving Routines and Precision Care
Critical Care Teams with a Life-and-Death Role
Critical care teams are at the front line of dealing with patients whose lives are at stake in the high stakes world of medicine. Such patients tend to be fighting critical trauma, multi organ failure, sepsis, or highly developed chronic illnesses. They are who require minute-by-minute observation, intervention that is aggressive and specialized decision-making.
Caring of complex patients is not a trial-and-error subject but rather a science supported by team work, cutting-edge technology, clinical excellence, and empathy. In this blog, protocols, staffing, equipment, communication, and ethical considerations will be investigated concerning how critical care teams deal with such vulnerable patients.
Let us get behind the curtain of an ICU or mobile critical care transport unit and discover how complexity, crisis, and care are navigated by these teams.
1. What are High Risk Patients?
Patients that are classified as high risks are at high risk of rapid degeneration or mortality because of:
- Extreme traumatic or injuries (e.g. car accidents, gunshots)
- Acute heart failure, liver, lungs, kidneys failure
- Sepsis or body infections
- Post operative complications
- Terminal sickness
- Severe breathing difficulty
- Neurological complication such as cerebrovascular accident or brain damage
These patients may have a need of:
- Invasive monitoring ( central lines, arterial line )
- Mechanical ventilation
- Continuous IV medication infusions
- Expression at the fast surgical or procedural interventions
- 24-hour nursing support and constant reassessment
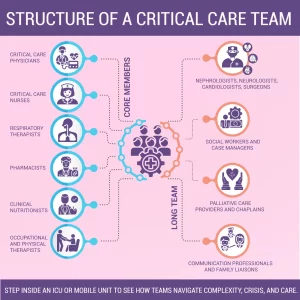
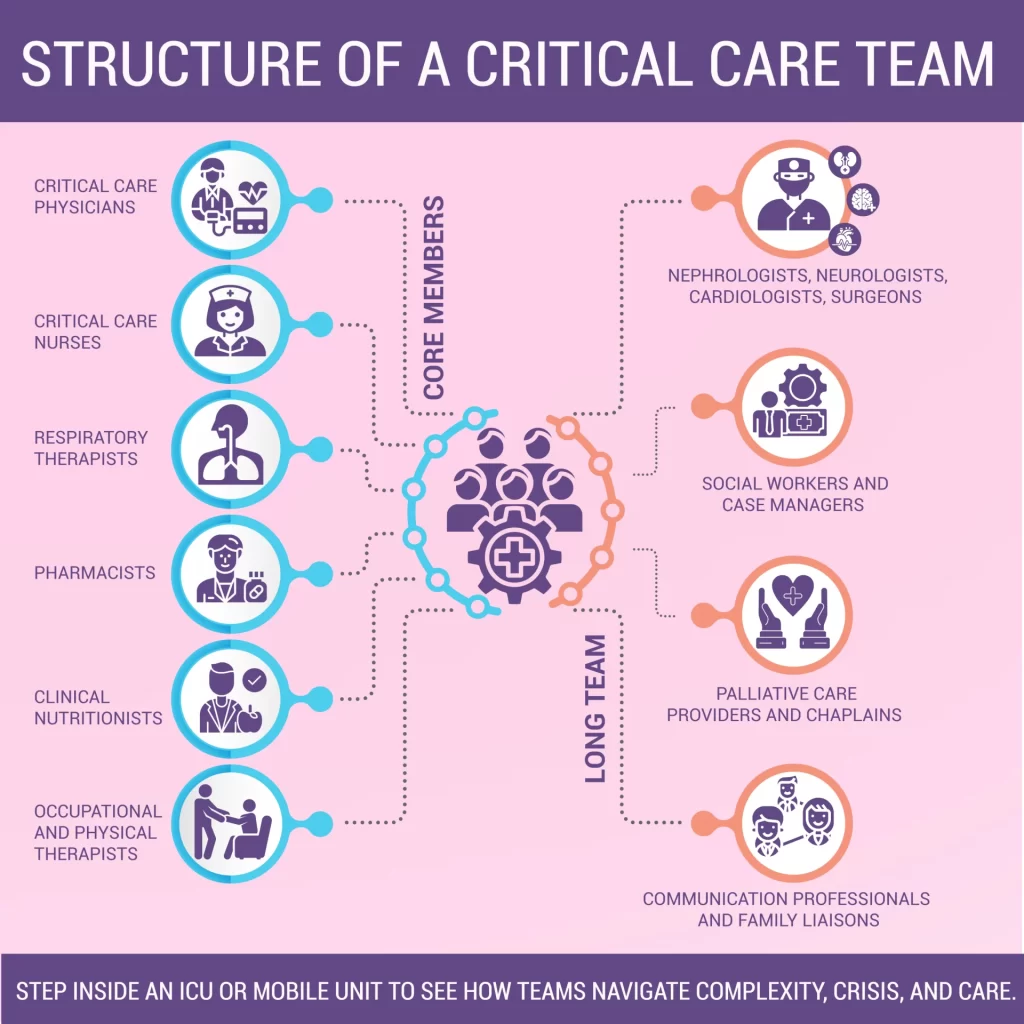
2. Structure of a Critical Care Team
A. Core members
- Critical Care Physicians (Intensivists): The core role of Critical Care Physicians (Intensivists) is to take charge of the care of the patient, identify the illness, and make the highest-order decisions about treatment.
- Critical Care Nurses: Perform bedside monitoring and administration of medication as well as implementation of care plans.
- Respiratory Therapists: Responsible over ventilators and provision of oxygen.
- Pharmacists: Tailor medication prescription, including interaction and vital dosing.
- Clinical Nutritionists: Make sure the body is provided with adequate nutrition needed to heal and immune response.
- Occupational and Physical Therapists: They assist in providing relief early mobilization and rehabilitation.
B. Long Team
- Nephrologists, neurologists, cardiologists, surgeons
- Social workers and case managers
- Palliative care providers and Chaplains
- Communication professionals and family liaisons
3. Admission and Triage: The Level of Care
Upon arrival in a hospital or being brought to medical expediency by the critical care transport team such as Infina Health, the initial process is the triage.
A. Triage Protocols
· Scores of acuity like APACHE II or SOFA
· Blood pressure and laboratory values
· Multi organ failure present
· Eminent danger to life
This enables the teams to:
· Prioritize care
- Bed assignment Pre ICU or step-down units
- Rally up equipment and personnel accordingly
4. Monitoring and Diagnostics:
An Eye of Every Second The critical care is facts-based. Each second is important and each variation is crucial.
A. Continuous Monitoring Systems
Heart rhythms ECGs
- Arterial lines blood pressure
- Hypoxemia through pulse oximetry and ABGs
- Monitors of intracranial pressure
- Central venous pressure (CVP)
B. High-End Imaging and Laboratory Work
- CT/MRI of the head or internal haemorrhage
- Chest X-rays abdomen X-rays
- Daily labs to check organ performance, electrolytes or markers of infection
It is aimed at getting good signs of any decline early enough.
If you want to get the precise critical care services for yourself or your loved ones then Infina Health is a perfect platform to book your services.
5. Interventions that Save Lives: Seconds Count
A. Respiratory Support
· Oxygen Treatment (nasal cannulas to non-rebreathers)
· BiPAP/CPAP Non-invasive ventilation
· Mechanical ventilators
· Prone methods of treating ARDS patients
B. Heart Support
- Low blood pressure IV vasopressors
- Antiarrhythmic medications on heart rhythm disorders
- Intra-aortic balloon pumps
- In severe cases the use of ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)
C. Renal Support
- Repeated Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT)
- Hemodialysis
D. Control of Infection
- Clinical regimens of antibiotics
- Isolation precautions
- Only sterile technique on any intervention
6. Communication and Collaboration
A Team Sport To work with a critically ill patient, there should be perfect coordination of all the departments.
A. Interdisciplinary Rounds Daily
Each morning the team sits and:
- Lab review vitals
- Discuss progress
- Revises care plans
- Establish 24-hour goals
B. Communications within the Family
Critical care personnel provide regular, genuine, and caring communication to the families particularly in end of life considerations or in matters dealing with codes.
7. Palliative and Ethical Decision-Making
A. Patient Autonomy
- The advance directives and DNR (Do Not Resuscitate) orders are respected.
- Capacity evaluations will be carried out in case the patients are not able to communicate.
B. Early Palliative Care Introduction
In situations when recovery is unlikely, palliative care comes in to:
- Control symptoms and pain
- Enable the proper end-of-life treatment
- Assist emotional and spiritual health
Critical care is not necessarily aggressive care, but it is the sound judgment that is ethically responsible.
8. Critical Care Transport: ICUs in the Mobile Environment
There is also Critical Care Transport Teams offered by service providers such as Infina Health, where transfers are staffed with ICU-level care expertise.
A. Special Transport Units
They have ventilators, defibrillators, infusion pumps
Critical care paramedics, nurses, and occasionally physicians staff them
B. Usual Situations
- Transporting a trauma patient in rural hospital to a trauma centre
- Transporting a post-operative patient in a long term ICU
- Assistance of the neonate or paediatric critical patients
- Such teams guarantee continuity of care at times when a patient is at his or her most vulnerable in the patient journey.
9. Transformational Technology
A. Artificial Intelligence and predictive analytics
Machine learning models have the ability to predict:
- Sepsis onset
- Risk to re-intubate
- The risk of cardiac arrest
B. Tele-ICU platforms
In rural hospitals or during periods when hospitals are overwhelmed, there is a remote intensivist (who observes patients through cameras and software).
C. Smart Infusion pumps and closed systems
These reduce human error and make the delivery of drugs to be optimum.
10. Post-Critical Care Rehabilitation
It is not the end of the road once a certain patient goes out of the ICU.
A. Post-ICU Syndrome (PICS) Patients can encounter:
- Muscle weakness
- Cognitive issues
- PTSD / anxiety
B. Transition between Care
- Stepdown units
- Rehabilitation or home care centres
- Specialty and primary care follow up
- Critical care units plan recovery since Day 1.
11. Training and Simulation: Worst of the Best
To deal with the situations (rare but lethal) that occur occasionally, critical care teams receive extensive lifelong learning:
- Mock codes, airway drills and high-fidelity simulation training
- Certification course (ACLS, CCRN, FCCS)
- Learning complex cases through Morbidity and Mortality conferences
The course of training on the subject is continuous and never-ending at Infina Health and in most hospitals of the country.
The Unseen Heroes of Critical Care
High-risk patients are a very challenging, exhaustive, and emotionally draining task – yet one of the most rewarding ones. The science, skill and soul that critical care teams apply to rescue patients at the point of death or right before death is what they are all about returning someone to life when they can and when not providing soul and dignity in the process.
Either in an ICU of a hospital or being inside a rolling ambulance with Infina Health being inside, these professionals have life in their own hands.
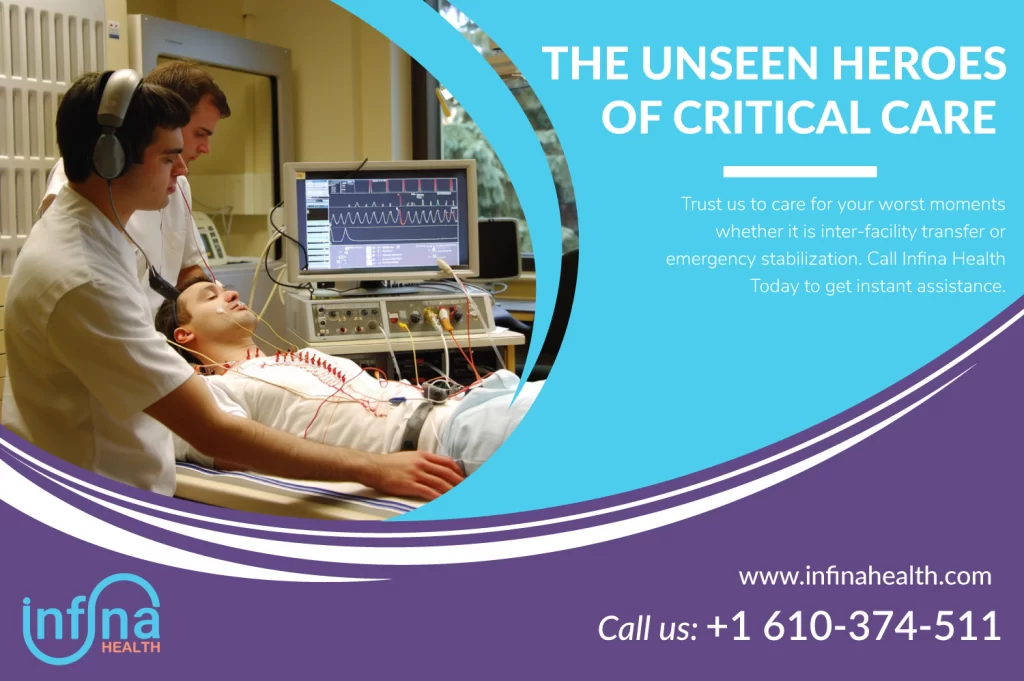
Do you need professional care on the go?
The Critical Care Transport Teams of Infina Health provide highly qualified professionals and devices of the ICU level to your home.
Trust us to care for your worst moments whether it is inter-facility transfer or emergency stabilization. Call Infina Health Today to get instant assistance.