How Critical Care Transport in Lehigh Valley Differs from Other Services
When it comes to medical transportation, not all services are created equal. While basic transport can meet the needs of many patients, critical care transportation (CCT) is designed for those who require specialized, life-saving support during transit. In regions like Lehigh Valley, where medical services are highly specialized, the need for critical care transportation is more pronounced than ever. This article will explore how critical care transport in Lehigh Valley differs from other medical transport services, the technology and expertise behind it, and why it’s essential for patients.
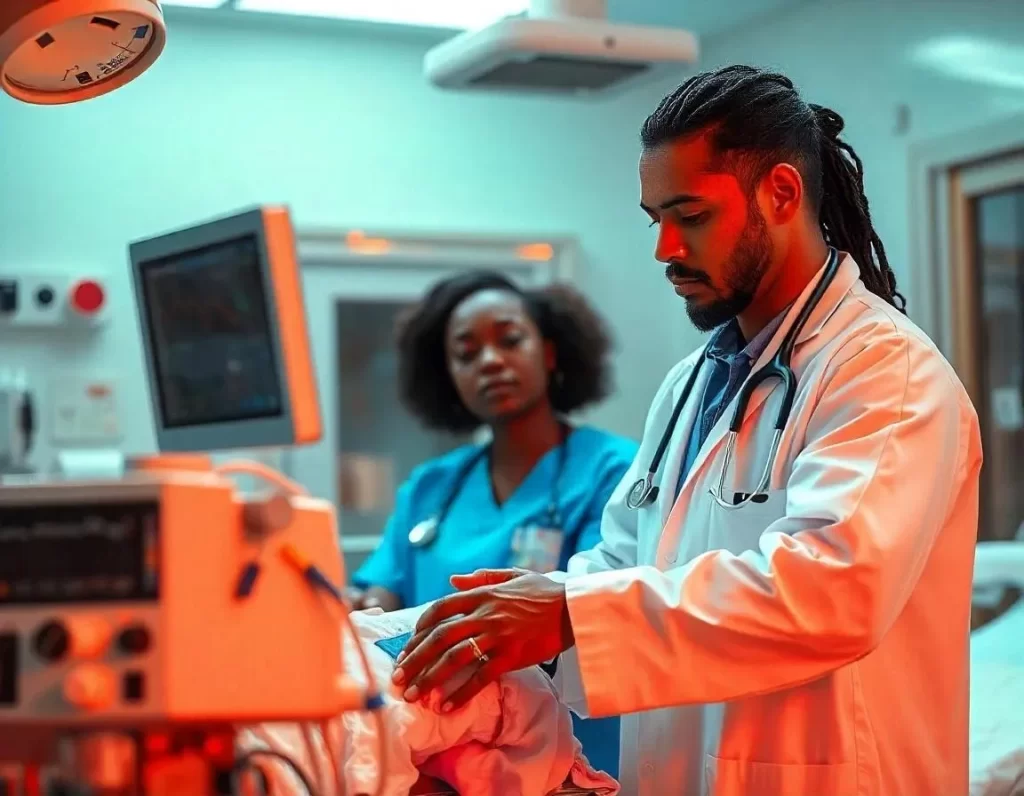

Two medical professionals performing life-saving procedures during critical care transport to stabilize a patient.
What is Critical Care Transport (CCT)?
Critical Care Transport (CCT) is a specialized service that provides the highest level of care during medical transport. It is designed for patients who are critically ill or severely injured and need constant monitoring, advanced medical interventions, or specialized care while being transferred to or between healthcare facilities. This includes patients requiring intensive monitoring, ventilator support, intravenous medications, or life support systems.
In Lehigh Valley, CCT services are typically utilized for patients experiencing conditions such as:
- Heart attacks (Myocardial infarctions)
- Strokes
- Severe trauma injuries
- Respiratory failure or complications
- Post-surgical complications
- Organ transplants
- Burn injuries
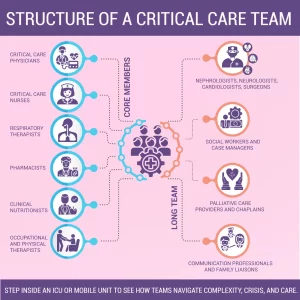
CCT involves the use of specialized vehicles, such as fully equipped ambulances or air transport, manned by highly trained medical professionals, including paramedics, nurses, and physicians. The key distinction between CCT and other types of transport services is the level of medical support provided during transit.
Is your patient in need of critical care transport? Reserve your service with Infina Health.
The Difference Between Critical Care Transport in Lehigh Valley and Other Medical Transport Services
To fully understand the value of Critical Care Transport, it’s essential to compare it with other types of medical transport services. Let’s break down how CCT differs from services such as Basic Life Support (BLS), Advanced Life Support (ALS), Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT), and Wheelchair Transport.
1. Critical Care Transport vs. Basic Life Support (BLS) Transport
Basic Life Support Transport is the most basic form of emergency medical transportation. BLS transportation services are typically provided by EMTs (Emergency Medical Technicians) who offer non-invasive medical care, such as CPR, basic wound care, and oxygen administration. BLS is ideal for patients who are stable but may require transport to a healthcare facility for non-life-threatening conditions.
Key Differences:
- BLS: No advanced life support equipment; mainly focused on providing basic care (e.g., oxygen, basic monitoring, CPR).
- CCT: Equipped with advanced life support equipment such as cardiac monitors, IV pumps, ventilators, and medications to manage life-threatening conditions during transport.
In essence, BLS is for stable patients, while CCT is for critically ill or unstable patients.
2. Critical Care Transport vs. Advanced Life Support (ALS) Transport
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Transport provides a higher level of care than BLS, typically performed by paramedics with specialized training. ALS services include interventions such as advanced airway management, defibrillation, and medication administration. While ALS offers more advanced care than BLS, it may not always be sufficient for the most complex medical cases requiring continuous monitoring and intervention.
Key Differences:
- ALS: Provides advanced interventions but may not offer the same intensive care as CCT. ALS vehicles are typically staffed by paramedics and may carry advanced medical equipment.
- CCT: CCT teams consist of medical professionals such as critical care nurses or physicians and are equipped to provide continuous, intensive care. CCT is more suited for life-threatening emergencies where constant monitoring and complex interventions are required.
In summary, ALS is suitable for patients requiring more advanced care than BLS, but CCT goes even further by providing intensive care and life support in transport.
3. Critical Care Transport vs. Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT)
Non-Emergency Medical Transportation (NEMT) is designed for patients who are stable but need assistance traveling to or from healthcare appointments, such as routine doctor visits, physical therapy, or dialysis. NEMT does not involve the use of medical equipment or personnel. Patients may be escorted by a driver or a non-medical assistant, but there is no medical oversight during the journey.
Key Differences:
- NEMT: For non-urgent, routine medical trips. Vehicles are not equipped with medical equipment, and there is no medical supervision during transit.
- CCT: For patients with life-threatening conditions requiring continuous monitoring, interventions, and specialized care. CCT vehicles are equipped with advanced medical equipment and staffed with critical care professionals.
While NEMT is for stable patients needing transportation for less critical reasons, CCT is essential for those facing serious health crises that require immediate and constant medical attention.
4. Critical Care Transport vs. Wheelchair Transport
Wheelchair Transport is a service designed for patients who have mobility challenges but do not necessarily require medical attention during transport. This service is often used by elderly patients or individuals with disabilities who need assistance getting to medical appointments, rehabilitation centers, or other locations. These vehicles are equipped with ramps and wheelchairs, and the driver may assist with transferring the patient.
Key Differences:
- Wheelchair Transport: Provides transport for patients who need mobility assistance but are otherwise stable and do not require medical care during the journey.
- CCT: Involves transport for critically ill patients who need intensive medical support and monitoring. These vehicles are equipped with specialized medical equipment such as oxygen tanks, cardiac monitors, and ventilators.
The main difference is that wheelchair transport is focused on ease of mobility, while CCT is focused on life support and medical care during transport.
The Importance of Critical Care Transport in Lehigh Valley
Lehigh Valley is home to some of Pennsylvania’s leading hospitals, including Lehigh Valley Health Network and St. Luke’s University Health Network, which provide cutting-edge healthcare services. However, when a patient’s condition is critical, access to specialized transport becomes essential. Critical care ambulance ensures that patients receive uninterrupted medical care while being transferred between facilities or to more specialized care units.
For example, if a patient in Lehigh Valley requires an organ transplant and needs to be transported to a larger, specialized hospital, they need more than just basic transport. The journey may span several hours, and during that time, the patient could experience life-threatening complications. A critical care transport team with the right equipment and medical expertise is crucial to ensuring that the patient’s condition remains stable throughout the transfer.
Why Choose Infina Health for Critical Care Transport in Lehigh Valley?
Infina Health is proud to offer some of the most reliable and advanced critical care transport services in Lehigh Valley. Our services stand out because of the following:
- Highly Trained Staff: Our critical care transport team consists of experienced paramedics, critical care nurses, and physicians, all trained in critical care, ACLS (Advanced Cardiac Life Support), and trauma care. We’re prepared for any emergency and can manage complex medical conditions during transport.
- State-of-the-Art Equipment: Infina Health provides cutting-edge medical equipment, including portable ventilators, cardiac monitors, infusion pumps, and other life-saving devices that ensure continuous care throughout the transport process.
- 24/7 Availability: Emergencies don’t happen on a schedule, which is why Infina Health offers round-the-clock critical care transport, ensuring that patients in the Lehigh Valley can always get the care they need, no matter the time of day or night.
- Local Knowledge and Connections: We are deeply embedded in the Lehigh Valley community, which means we understand the local healthcare system, including key hospitals, trauma centers, and medical facilities. This allows us to provide seamless transitions for patients requiring specialized care.
Conclusion
When it comes to critical care transportation, not all services are equipped to handle the complexity and urgency of life-threatening medical conditions. Infina Health sets itself apart by offering the highest level of care, with fully equipped vehicles, highly trained medical staff, and a commitment to patient safety and comfort. Whether you’re dealing with a traumatic injury, a medical emergency, or the need for intensive monitoring during transport, Infina Health has the expertise and resources to ensure the best possible care during your critical journey.
Your health and safety are our top priority. If you or a loved one requires critical care transport in Lehigh Valley, don’t hesitate to contact Infina Health.