How ALS Teams React as Compared to BLS Teams
In a medical emergency, minutes and even seconds can mean the difference between life and death, and the nature of prehospital care team sent can affect an outcome. Nearly everyone is familiar with an ambulance when they see one, but not many people realize that there are two categories of emergency medical care that have different responsibilities and capabilities–the first level which is Basic Life Support (BLS) and the second one being Advance Life Support (ALS).

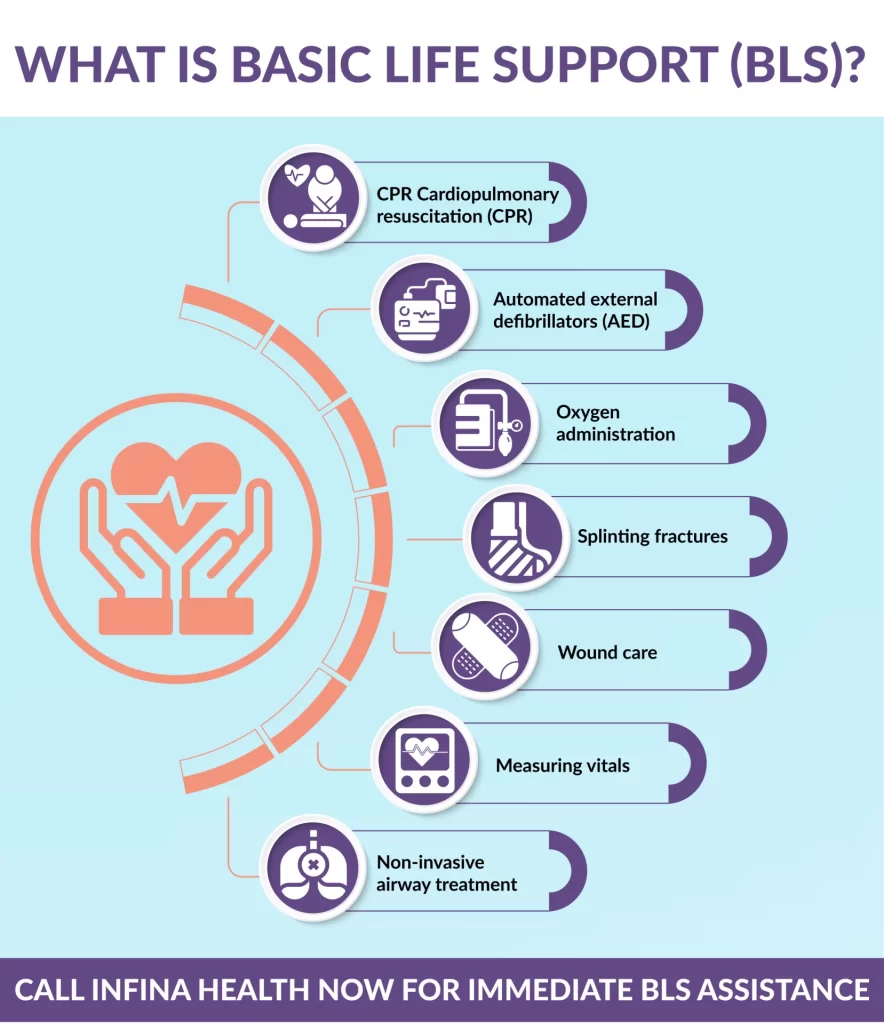
What Is Basic Life Support (BLS)?
Basic Life Support (BLS) means non-invasive urgent care given by Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs). BLS is aimed to support the patient in a rather stable state or not-so-critical conditions and is conducing to the basic prehospital care that includes:
- CPR Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)
- Automated external defibrillators (AED)
- Oxygen administration
- Splinting fractures
- Wound care
- Measuring vitals
- Non-invasive airway treatment
BLS providers are not allowed to manage other medications outside oxygen, glucose (diabetes patients) or epinephrine using an auto-injector. They are not meant to perform advanced treatment; their job is stabilization and transportation.
What is Advanced Life Support (ALS)?
Advanced Life Support (ALS) It is a superior form of prehospital care usually administered by paramedics or critical care nurses who have received special training in advanced operations and drug administration. ALS teams are prepared and trained in life-threatening emergencies, which include:
- Cardiac arrest
- Stroke Respiratory failure
- Severe trauma
- Poisoning or overdose
- Seizures
- Important elements of ALS care are:
- IV therapy
Advanced airway intervention (e.g. endotracheal intubation)
- The interpretation of electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Monitoring and defibrillation of the heart
- Pain, seizures, sedations, arrhythmia, etc., treated with drugs.
When every second counts, trust Infina Health ALS teams to provide the expertise in care.
Training and certification: ALS and BLS
| Category | BLS (EMTs) | ALS (Paramedics) |
| Education Time period | 120–150 hours | 1,200–1,800+ hours |
| Certification | NREMT (EMT level) | NREMT (Paramedic level) |
| Medication Use | Very little (e.g., glucose, epinephrine auto-injector) | Very extensive (e.g., morphine, cardiac medication, sedatives) |
| Airway Management | Basic (oropharyngeal /nasopharyngeal) | Advanced (intubation, ventilators) |
| ECG | No | Yes |
| IV Access | No | Yes |
Paramedics receive 10-15 times the number of training hours than those of EMTs and are qualified to conduct intricate life-saving preoperative procedures.
Clinical Decision-Making and Scene Assessment
Clinical judgment and scene triage is one of the most important distinctions.
BLS Teams:
- Concentrate on stabilizing the patients and fast transport.
- Stick to the rigorous procedures of trauma, cardiac, and stroke evaluations.
- Reach out to ALS in case the condition of the patient deteriorates.
ALS Teams:
- Conduct diagnostic practices on occasions.
- Start critical interventions prior to coming to the hospital.
- Select between transporting a patient urgently and stabilizing them on the spot.
In many cases ALS teams also collaborate with hospitals and consult doctors over the air to achieve an immediate plan of treatment.
Medication Administration
A large difference in this is:
BLS Teams can give:
- Oxygen
- Oral glucose
- EpiPen epinephrine
- Aspirin (protocol)
ALS Teams are able to administer:
- IV fluids
- Medications of the heart (e.g. atropine, epinephrine, amiodarone)
- Pain killers (i.e., morphine, fentanyl)
- Anti-seizure medications
- Intubation sedatives
- Opioid overdose naloxone (Narcan)
It is an increased pharmacological toolset that allows ALS providers to delay or reverse life-threatening symptoms in real-time.
Coordination and Communication
BLS Teams:
- Inform hospitals and dispatch about the fundamental data.
- Make a request of ALS to support during escalation.
ALS Teams:
- Liaise with trauma centres, stroke centers and cath labs.
- Give precise reports with ECG results and medicines changes.
- Frequently serve as point-medical responders in highly complicated multi-victim situations.
Equipment Difference
BLS Ambulances are Supplied With:
- AED Oxygen tanks
- Suction devices
- Simple airway devices
- Stretchers and splints
- First aid kit
Other Features of ALS Ambulances:
- Reduced cardiac monitors/ defibrillators (12- lead ECG)
- Complex breathing devices (laryngoscopes, intubation tubes)
- IV-Infusion pumps syringe
- Medication packages
- Portable ventilators
- CO2 monitoring, Capnography
The high-tech arrangement of ALS vehicles has prompted them to be referred to as some of sort of mobile ICUs.
Real World Response Situations
Scenario 1 Chest Pain
- BLS Response: Oxygen, monitoring the vitals, fast transport, and simple CPR upon requirements.
- ALS Response: IV access, ECG, cardiac med, nitroglycerin, issue defibrillation.
Scenario 2: Seizure
- BLS Response: Airway, oxygen, transport following the termination of episode.
- ALS Response: IV benzodiazepines to arrest protracted convulsions, advanced airway on the off chance that unconscious.
Scenario 3: Auto Accident with Shock
- BLS Response: Spine positioning, spinal immobilisation, bleeding control and transportation.
- ALS Response: IV fluids, analgesia, oxygen, monitor shock, do advanced airway support, as needed.
At What Point Do ALS Teams Go?
Depending on location and protocol, dispatch decisions consist of the following:
ALS is sent on:
- People in an unconscious or un-responsive state
- Heart attack or chest ache Stroke symptoms
- Breathing difficulties
- Severe trauma
- Seizures
- Overdoses
There are systems that make both ALS and BLS go out simultaneously with unclear outcome. Others work with the tiered response systems when BLS is coming first, and ALS comes when necessary.
Patient Outcomes: The ALS Advantage
Research has revealed that:
- ALS care can reduce the mortality rate of cardiac arrests, trauma, and respiratory failures.
- In the short term, early administration of drugs, intubation, and ECG diagnosis leads to better survival and decreased complications in the long bet.
- ALS teams eliminate delays in the hospital by conducting procedures on the way.
Nonetheless, the excessive use of ALS in relatively non-serious situations may exert pressure on the resources, and this is the reason why triage and dispatching procedures are vital.
Summary: ALS vs. BLS Side by Side
| Feature | BLS Team | ALS Team |
| Provider Level | EMT | Paramedic |
| Training Hours | 120-150 | 1,200-1,800+ |
| IV Access | No | Yes |
| Medication | Limited | Detailed |
| ECG Monitoring | Yes | No |
| Decision-Making | Protocol based | Condition based |
| Priority of Dispatch | Stable patients | High acuity |
| Goal | Stabilize and transport | Stabilize, treat and follow along the way |
Final Thoughts
The contrast between ALS and BLS is not only on the level of equipment but on the scale, responsibility and life-saving power. The fast-changing environment of emergency medical services (EMS) means that the knowledge of such differences can make healthcare providers, patients, and communities understand the stratified nature of prehospital care.
It may be the normal transportation or life that is in the balance, but both types of EMS professionals remain committed to saving lives and delivering improved outcomes; one call at a time.
Want to Get ALS or BLS? Call Infina Health Now
At Infina Health, we provide Advanced Life Support (ALS) and Basic Life Support (BLS) high-tech transportation services custom to your medical requirements.
Our certified paramedics and EMTs stand ready 24/7 to work in non-emergency medical transport or a highly serious emergency, because in every case, time is an important factor and our paramedics and EMTs are prepared to give professional and compassionate care.
- Experienced ALS paramedic crews with licenses
- With state of the art cardiac and airway management equipment
- Effortless hospital/ physician liaison
- EMS in Pennsylvania that serves its communities with fast and certainly known EMS
It is our priority to provide you with health.
- Visit the Infina Health today through 1-888-446-3462
- Either get a transport appointment online at info@infinahealth.com