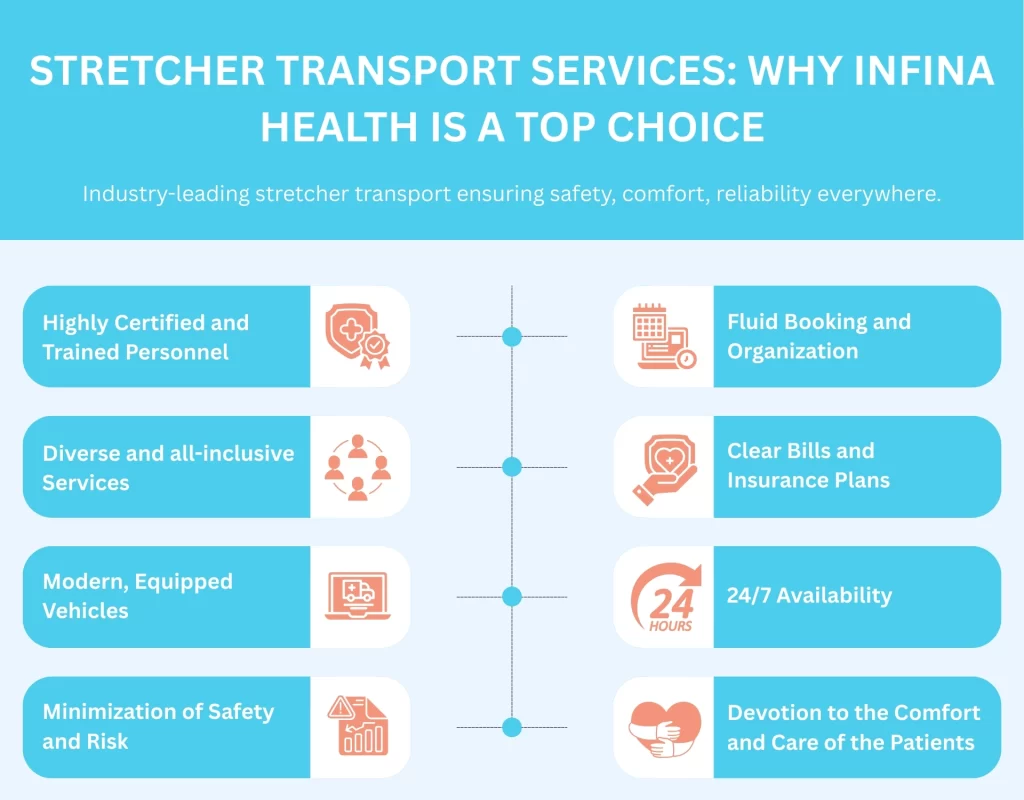
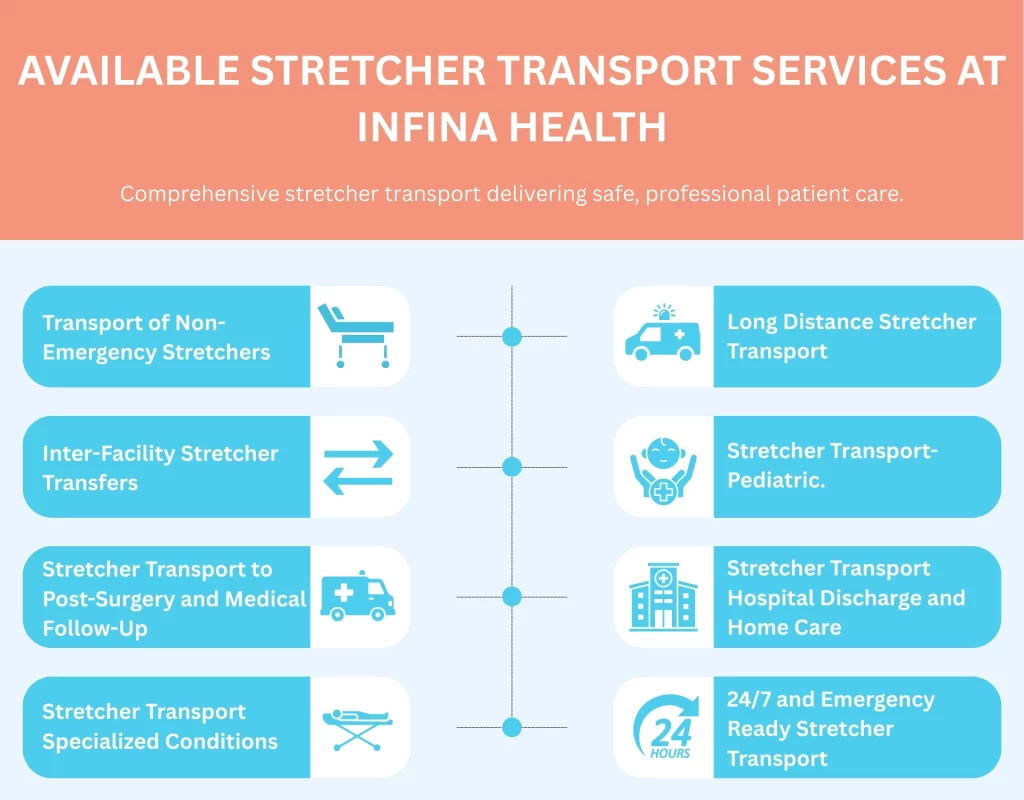
At Infina Health, we realize that the patients who need to be transported by stretcher have mobility problems, need high-level care, or are non-emerging conditions that need special attention. All our patients will find our services of transporting their stretchers to be safe, comfortable, and dignified to their hospital transfer, clinical appointment, or long-distance travel. Our team has been serving Reading, PA, Berks County, Lehigh Valley, Philadelphia, and vicinity with professional medical stretcher transportation which clients and families can rely on.
 Careers
Contact
BOOK NOW
Careers
Contact
BOOK NOW